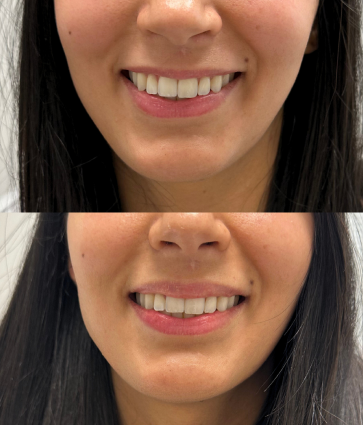
What are Neuromodulators?
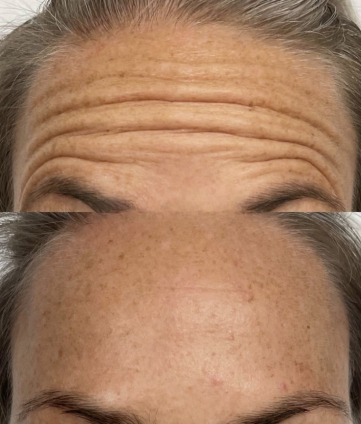
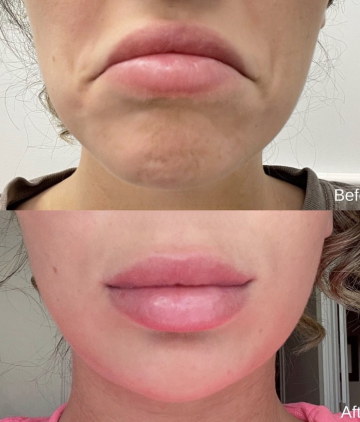
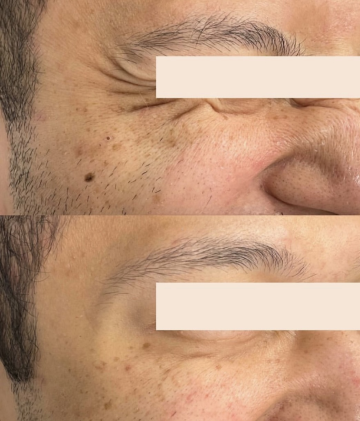
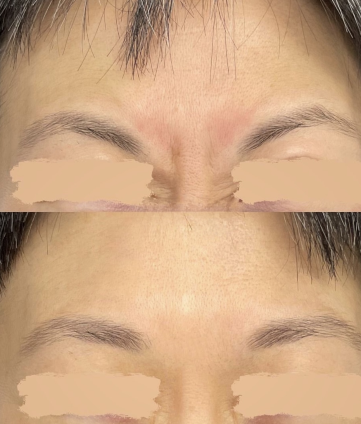
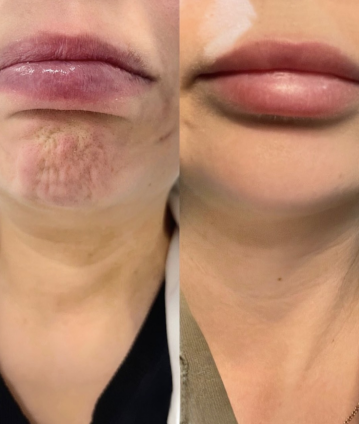
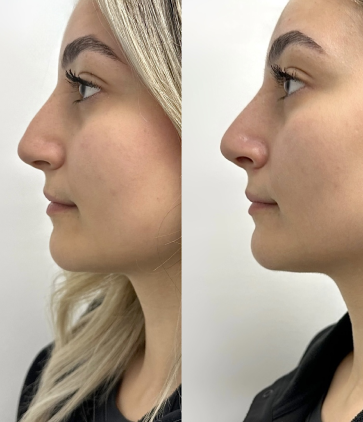
A very popular brand of neuromodulator, Botox Cosmetic (short for botulinum toxin) is a purified protein. It is used for various medical and cosmetic purposes due to its ability to cause temporary muscle weakness by blocking nerve signals in the muscles where it is injected. Medically, Botox is used to treat conditions characterized by excessive muscle activity such as muscle spasms, TMJ and certain types of migraines. Cosmetically, it addresses skincare concerns by reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles and fine lines as well as averting the upper lip and lifting the tip of the nose.
The Skin Studio Inc. proudly uses Botox Cosmetic as our preferred brand of neuromodulator.